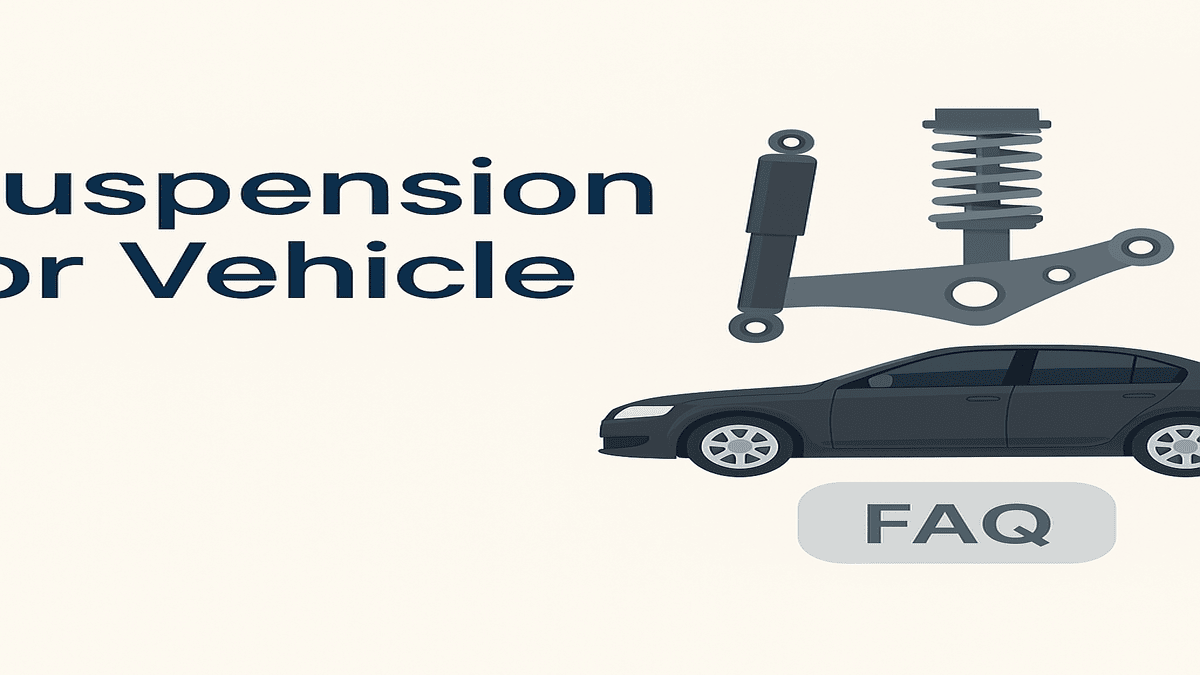
When it comes to the comfort, handling, and safety of a vehicle, few systems are as critical as the suspension system. Whether you’re navigating a bumpy road or cruising on the highway, your vehicle’s suspension ensures you experience a smoother ride, maintain control, and stay safe.
In this article, we’ll explore what a vehicle suspension system is, how it works, its major types, and when to get it inspected or replaced. We’ll also answer some common questions drivers have about suspension issues and upgrades.
What is a Vehicle Suspension System?
A suspension system is a collection of components, including springs, shock absorbers, struts, control arms, and ball joints, that connect a vehicle to its wheels. Its primary roles are to:
- Absorb and dampen road shocks from bumps and potholes
- Improve vehicle handling and stability
- Keep the tires in contact with the road for better traction and control
- Protect other components from excessive vibration and impact
Without a properly functioning suspension, your vehicle would be difficult to steer, handle poorly, and feel rough to ride in.
Main Components of a Suspension System
- Springs (Coil or Leaf Springs)
These bear the weight of the vehicle and absorb large impacts from road surfaces. - Shock Absorbers (Shocks)
Work alongside springs to dampen the motion and stop bouncing after hitting a bump. - Struts
Combine a shock absorber and spring in one unit, commonly used in front suspensions. - Control Arms & Ball Joints
Allow the wheels to move up and down while staying connected to the chassis. - Anti-Roll Bars (Stabilizer Bars)
Help reduce body roll when the vehicle turns or corners.
Types of Suspension Systems
- Dependent Suspension
Both wheels are connected via a solid axle. Found mostly in older trucks and off-road vehicles. - Independent Suspension
Each wheel moves independently, offering better comfort and handling. Common in modern cars and SUVs. - Air Suspension
Uses airbags instead of springs, providing adjustable ride height and superior comfort. - Hydraulic or Magnetic Ride Control
Found in luxury or performance vehicles, using advanced tech to adjust ride in real time.
Signs Your Suspension Needs Attention
Even the best suspension system will wear out over time. Look out for these symptoms:
- Vehicle pulls to one side
- Rough or bumpy ride
- Uneven tire wear
- Nose diving when braking
- Oily or damaged shocks/struts
- Excessive bouncing after bumps
- Poor steering response
If you notice any of these signs, it’s a good idea to visit a mechanic for an inspection.
How Often Should You Replace Suspension Parts?
There’s no exact rule, but typically:
- Shocks and struts: Every 50,000–100,000 miles
- Springs and other components: May last longer but should be inspected during regular service
Driving habits, road conditions, and vehicle load can affect how long your suspension lasts.
Suspension Upgrades for Better Performance
Some drivers choose to upgrade their suspension for better off-road performance, towing capacity, or sporty handling. Common upgrades include:
- Lift kits for higher ground clearance
- Performance shocks/struts for tighter control
- Lowering kits for improved aerodynamics and handling
- Air suspension kits for adjustability
Make sure any upgrades are installed professionally and match your driving goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What happens if I drive with a bad suspension?
A bad suspension affects braking, steering, and handling—putting you and others at risk. It also leads to uneven tire wear and could damage other vehicle parts.
Q2: Can I drive with broken shock absorbers?
Technically, yes, but it’s unsafe. Your car may bounce excessively, become hard to control, and take longer to stop. Replace them as soon as possible.
Q3: What’s the difference between shocks and struts?
- Shocks: Dampening components only.
- Struts: Combine shocks with a structural component (spring). They are integral to the vehicle’s suspension and alignment.
Q4: How do I know if my suspension is damaged?
Look for bouncing, uneven tire wear, noise over bumps, or the vehicle leaning to one side. A professional inspection will confirm the issue.
Q5: How much does it cost to repair a suspension system?
Costs vary:
- Shocks/struts replacement: $300–$800 per pair
- Full suspension repair: $1,000–$2,500 depending on the damage and type of vehicle
Q6: Is suspension covered under warranty?
If your car is under manufacturer’s warranty or an extended service contract, some parts of the suspension may be covered. Check your warranty details for specific terms.
Q7: Can I upgrade my suspension myself?
While minor upgrades like sway bars can be DIY projects, major suspension work should be done by professionals. Incorrect installation can be dangerous and costly.
Final Thoughts
Your vehicle’s suspension is more than just comfort—it’s safety, performance, and control all in one. Understanding how it works and staying on top of maintenance can prevent costly repairs and keep your ride smooth and stable.
Whether you’re daily commuting or planning off-road adventures, keeping your suspension in top shape ensures you’ll always be driving with confidence.